You want to encrypt an email in outlook?
The content is top secret and only the recipient should be able to read the message?
This guide will give you instructions.
Let’s start!
Why are normal (secure) emails not secure?
Secure IMAP / SMTP – encryption all the way to the server is secure.
The big problem is that only the route from your house to your email provider’s server can be secure. The transfer from the e-mail provider (e.g. yahoo) to the e-mail provider (GMX) could be done in CLEARTEXT.
The inventor of e-mail
Ray Tomlinson invented the e-mail in 1971.
He invented a communication channel that changed the world, and his primary goal was not to make e-mail secure, but functional.
E-mail is an evolved invention. Users love the ease of use and the “free” way of sending messages, if you ignore the cost of computers, electricity and internet.
Ray, however, had not considered making e-mail “secure”. He didn’t want to encrypt email.
Encryption was not necessary in the past ..
In 1971, most of us did not yet have the internet or even a computer. The “internet” at that time was mainly used by researchers, students and professors who used the net to exchange knowledge.
The “inventors of the Internet” did not want to create a network that everyone could access.
Steffen Lippke
What is the most secure email encryption?
The most secure encryption for e-mails is PGP encryption (Pretty Good Privacy).
Steffen Lippke
PGP is completely free to use and there are many mail clients on the market that use PGP. PGP is cryptographically secure because it uses end-to-end encryption.
An end user can trust PGP because the protocol uses end-to-end encryption. As a sender, you are not dependent on the security of your email provider. Any hacker, the NSA or a state reading the message will only see a jumble of letters (cipher).
What does end-to-end encryption mean?
End-to-end encryption ensures that only the recipient can read the message.
Even if the message is sent via an insecure channel, no one can deduce the message (plain text) from the data salad (cipher).
Such a transmission requires an asymmetric key pair. The sender encrypts the text with the publicly known key of the recipient. Only the private, secret key of the recipient can create a readable message from the data chaos.
Encrypting e-mail – PGP tutorial
Today I would like to show you how to use PGP.
- Go to https://www.gpg4win.de/index.html
- Download the latest version
- Install the software
- Start the software Kleopatra
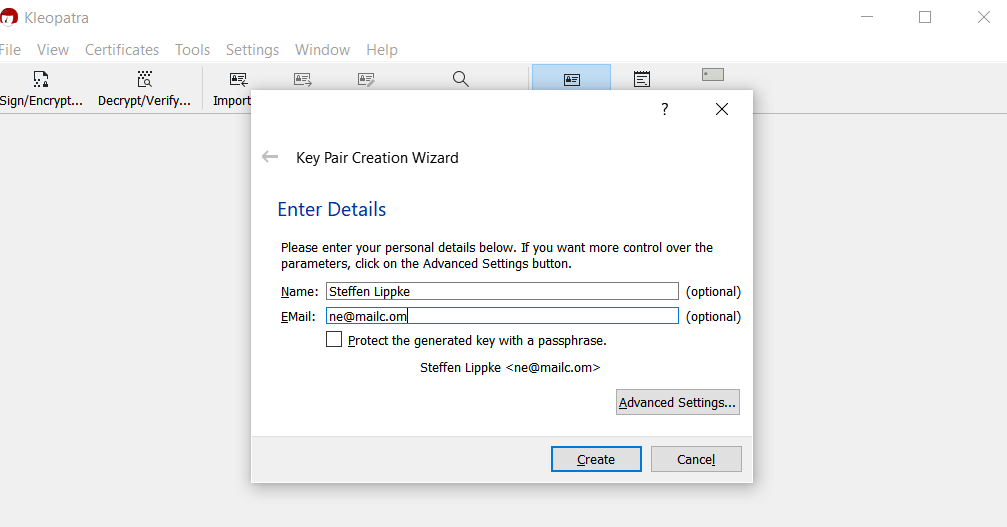
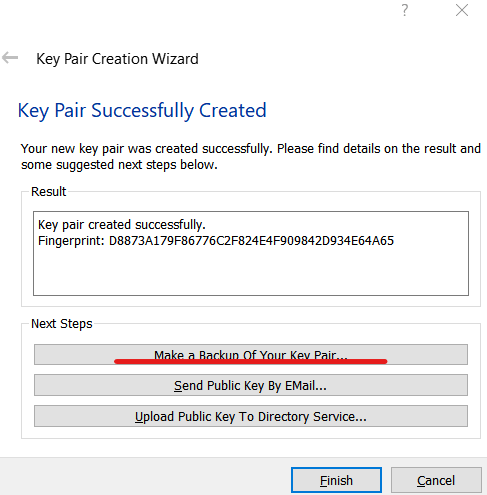
- Create a key pair with your name and email. Assign a password
- Save the key in a backup
- Open Outlook
- Create a new e-mail. Remember, you can only send an encrypted email to someone who uses PGP. The recipient must give you his or her public key first.
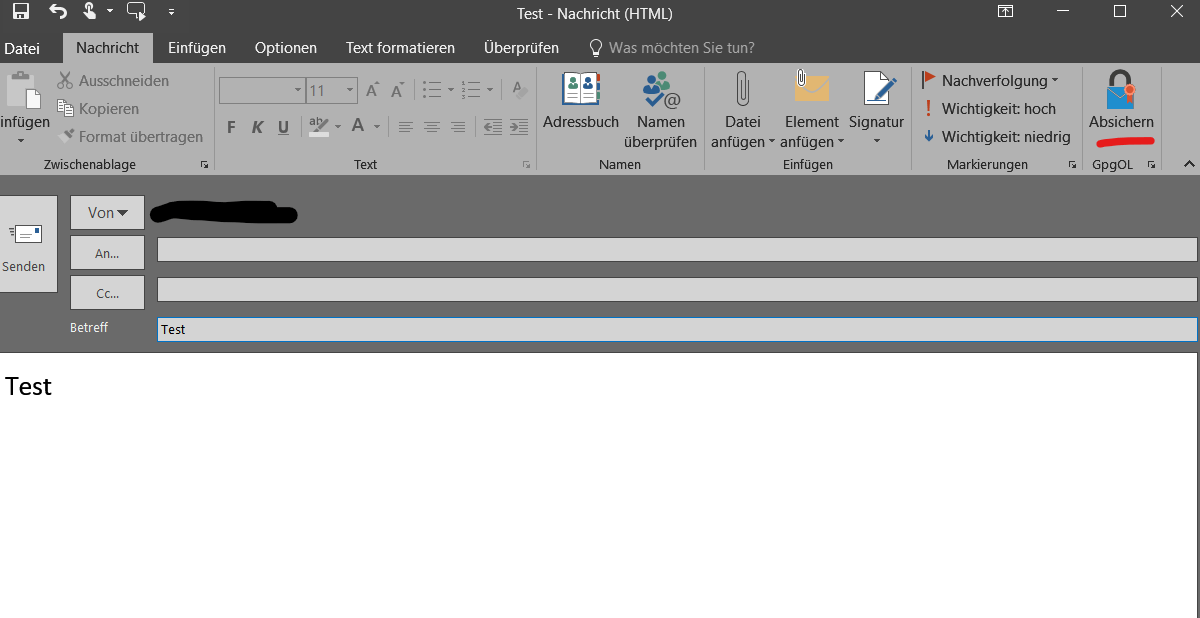
- Click on Secure –>
Encrypt in the upper right corner
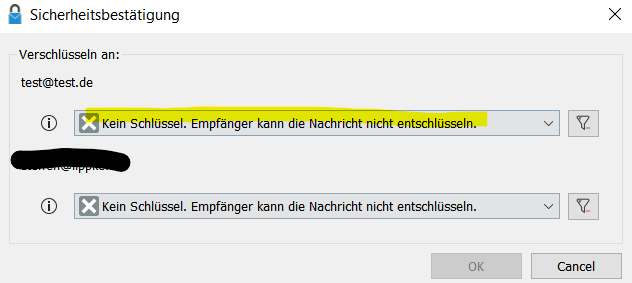
- Send the e-mail and check whether you have the other person’s public key.
Alternative: Thunderbird with OpenPGP
What are the disadvantages of PGP?
If PGP is secure, why is encryption so unknown? The following four reasons speak against PGP
- Understanding: Many people do not know that normal e-mail is insecure. Also, the concept of two keys is very confusing. Most people wanted to communicate first and foremost and are not concerned about security / think it must be secure.
- Reach: You can’t write a secure email to everyone on the fly. You need the other person’s public key. You have to convince the other party to use PGP.
- Backup: If you lose your private key, you can’t open PGP encrypted email anymore, you have to tell all your mail contacts that you have a new key.
- Usability: The principle of public and private keys is not intuitive. If you use PGP incorrectly, the encryption is in vain, e.g. if you send the private key, lose it or a criminal steals it.
What else can I do …
What is a practicable email encryption?
The best known alternative to PGP is S/MIME.
These email certificates use a Certificate Authority as a key master to help you.
The big disadvantage of S/MIME is that you have to buy a certificate. You can buy a certificate inexpensively for 20 to 80 euros per year. The certificates are divided into three quality classes.
- Class 1 can be obtained by anyone who has an e-mail address.
- Class 2 checks more and also includes the owner.
- If you want a class 3 certificate, you have to prove yourself to the Certificate Authority.
What is a Certificate Authority?
Most of the security on the internet rests on the fact that our browsers trust a few companies (Digicert, GlobalSign, Let’s Encrypt).
These companies, called Certificate Authorities, offer other companies to confirm the authenticity of their communications (emails) and company websites.
Your browser or mail programme asks the Certificate Authority each time to check whether the requested website is genuine.
PGP technology explained – encrypting e-mail
Why is this encryption secure? The following section explains how PGP makes it possible.
What is a public / private key?
With the recipient’s public key you can encrypt the message for the recipient. A third party cannot decrypt the message with the same key.
Only the recipient can decrypt the message with his private key. The message is only secure if the recipient has secured their computer from hackers. If another person has stolen the private key, the criminal can decrypt any email from the recipient.
Cryptographic keys can either lock (encrypt) or unlock (decrypt). A key can never decrypt and encrypt at the same time.
How legally secure are e-mails?
A normal e-mail can have a low probative value. However, courts would not always recognise it.
German jurisprudence recognises a digital signature as secure.
Steffen Lippke (No legal advice)
A digital signature is technically a reverse encryption.
The sender creates a digital fingerprint (hash) of his message text and encrypts it with his private key = signature.
Anyone else can form the same hash of the message text and decrypt it with the sender’s public key. This results in the same hash if the message originates from this person.
