How can I locate a mobile phone quickly and easily?
This guide explains 7 tracking methods to find your device again.
Let’s get started!
Tracking is not just GPS

If you are looking for a smartphone or a push-button mobile phone, you have the following seven options. Depending on the circumstances and requirements, you must choose one of the seven methods.
If one technology does not work, then another method will work. Depending on the use case and location, different technologies will help you.
Basic principles
The position of a mobile phone can be determined using electromagnetic waves. The digital signals transmit information (e.g. time). The following 4 basic principles will help you to understand why localisation is good, inaccurate or not at all:
- Strength or angle of the signal: the receivers can use the strength and angle of the mobile phone signal to determine the position more precisely. The sensors can form two straight lines that intersect. The intersection of the straight lines is the location of the device.
- Measuring the round trip time: For all forms of localisation, the devices need a very precise stopwatch and time in order to calculate the distance from the signal transmission time. Electromagnetic waves move constantly at the speed of light. The distance is the time t × 300,000 km/s
- Barriers make it difficult to determine the position: Conductive materials make communication more difficult because the electromagnetic waves can only penetrate these materials with difficulty. The transmitters would have to send a stronger signal or a signal with a different frequency. Stronger signals increase the power requirement so that your smartphone battery runs out more quickly.
- More receivers are better: The more devices that connect to your mobile phone, the more accurate the location will be. If one of the receivers measures incorrectly or has other errors, the algorithm can exclude it from the localisation process. A variety of communicators help to minimise the circular area in which the device must be located.
The classic – Global Position System (GPS)
When most people think of navigation systems, the first buzzword is GPS: the Global Position System (GPS) helps devices on earth to determine their position. Three satellites are sufficient to determine the position on the globe. The satellites transmit their location and time via a specific frequency.

For the last few decades, we have been using the inaccurate and outdated NAVSTAR GPS system from the USA. Since 2016, new devices have been able to receive signals from Galileo (a satellite network of European and Russian satellites).
Accuracy: NAVSTAR GPS offers a 10-metre radius accuracy, while Galileo GPS determines the position to within a few centimetres.
Apps: Android Google’s“Find device“, Apple’s“Where is app“, own antivirus apps offer a find function
Requirement: You need a smartphone with a functioning GPS chip, which should be installed in most devices (at least NAVSTAR GPS). The device must be outside (or under a pane of glass). Positioning will fail if the device is surrounded by reinforced concrete, for example.
The flexible solution – wireless LAN
Indoor navigation, e.g. in exhibition halls, shopping malls or airports, is ideal for this purpose. The operator sets up wireless LAN routers in all corners to which the smartphones connect. The routers are located on a map so that 3 or more routers determine the location of the smartphone.
Accuracy: You can locate devices with an accuracy of 5 to 14 metres
Requirement: The smartphone must be in the area of a controlled network and the Wi-Fi must be switched on.
Silence – Global System for Mobile Systems (GSM)
Positioning does not necessarily require satellites buzzing around in space.
Mobile phone masts on earth can locate smartphones and old push-button mobile phones with an accuracy of up to 50 metres. GSM (Global System for Mobile Systems) positioning is possible wherever you have mobile phone reception.
Accuracy: Cell ID: several kilometres’ radius, E-OTD / U-TDOA: 25 m radius
Requirement: A mobile radio module should be installed in every mobile phone. This positioning may not be used for civilian purposes without good reason. For example, the police may use this positioning if the mobile phone is connected to a criminal offence (e.g. kidnapping). They use “silent SMS” for this purpose. A smartphone does not display silent text messages, but connects to the nearby masts.
Apps: Some navigation apps such as HERE Maps use GPS and GSM localisation at the same time. You can use this special app to locate the “transmission cell” in which the smartphone is currently located.
The exact one – Bluetooth
Similar to W-LAN positioning, Bluetooth receivers must be distributed in the neighbourhood in order to register the smartphone. Bluetooth has a weaker signal and only reaches 100 metres with eye contact or through a thicker wall. Bluetooth is available in two types:
- Low energy technology: Enables a device to be located in a power-saving way.
- Angle of Arrival: The receivers recognise the direction from which the signal is coming. Two receivers can use the straight line intersection to determine the location of the device.
Accuracy: 1-3 metres
Requirement: The smartphone must be within range of the Bluetooth receivers. This type of localisation is used in large buildings. If you have lost your mobile phone, for example, the building administrator can help you (you should know the Bluetooth ID).
Use: Try positioning at CCC conferences with c3nav or in shopping malls with the InMapz indoor app.
The cryptic one – fingerprinting
This form of localisation is interesting for website owners. Location tracking is useful for blocking unauthorised login attempts or tracking down a hacker. Every time you visit a website, your browser sends characteristics of your computer to the server:
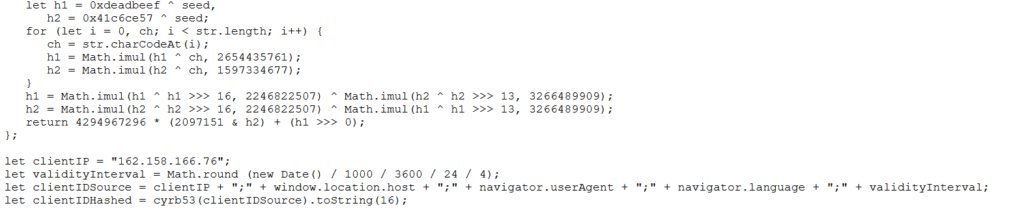
- Screen size
- Browser type
- Encryption types, internet protocols
This data helps the website operator to determine the device being searched for via the Internet and the router.
z. E.g. 100 devices are registered in the target W-LAN. Only 1 device has a resolution of 2440×1080 and the Opera browser is installed.
Steffen Lippke
Accuracy: Ideally up to the end device – in the worst case up to the VPN provider.
Prerequisite: You must have access to the logs.
The tracing – geotargeting
If your device (mobile phone, desktop, notebook) is connected to a Wi-Fi network, the signal can be traced back to the device’s router. Because you can only use your device in the immediate vicinity of the Wi-Fi router, the positioning is relatively precise.

Accuracy: You can locate the device up to a neighbourhood, city or, if you are lucky, up to the building.
Prerequisite: Special software enables your mobile phone to call home via the Internet and communicate the IP address of the Wi-Fi. You can roughly localise the IP address via the website http://www.utrace.de/ or https://www.infosniper.net/index.php?lang=2. For a more precise analysis, you would have to file a report with the police
The unknown – external positioning
If all previous methods have not helped, consider whether the device is very likely to be located together with other sensors, e.g:
- Your smartphone and laptop were stolen together. Locate your laptop.
- Your device is in a modern car. You may be able to locate the car.
- Another mobile phone was stolen with your device.
Accuracy: As accurate as the external device can be located.
Prerequisite: A second sensor exists.
